Automotive SPICE
Automotive SPICE
What is Automotive SPICE?
Automotive SPICE® (System/Software Process Improvement and Capability dEtermination) is an industry standard introduced to help OEMs and their suppliers to manage the complexity in processes based on best practices and lessons learned.
Automotive SPICE is a process assessment model (PAM). ISO 33002 is the norm for assessments. These assessments use a PAM as reference to compare the process activities in a real project of a software based system with the base practices (capability level 1) and the generic practices (CL 2-5). The process ratings with their evidences is then documented in the assessment report signed by the lead assessor.
With growing complexity in car components, most car manufactures and their TIERs require development in line with Automotive SPICE (ASPICE) capability level CL2 or even CL3. Projects have often hundreds of engineers involved. Thousands of requirements need to be analyzed and later qualified in system tests. Processes in line with Automotive SPICE ensure quality output in line with defined milestones.
Automotive SPICE® is a trademark of VDA QMC www.automotivespice.com.
![]()
What are the ASPICE Capability Levels?
The process assessment model (PAM) of Automotive SPICE defines base practices for capability level CL1 and general practices for higher capability levels. In ASPICE assessments, the rating of these practices is used to determine the capability level of a particular process in the assessment scope.
There are five capability levels: CL1 – Performed. CL2 – Managed. CL3 – Established. CL4 Predictable. CL5 – Innovating.
![]()
What is the goal of Automotive SPICE?
The motivation for companies to use ASPICE in their development:
Increase quality
- Work products (WPs) are based on qualified input
- WPs are verified and validated based on criteria
- WPs are produced as planned and scheduled
- Organizational Learning due to improved standards
Reduce cost
- Early identification and correction of lacks
- Proven processes and templates; experienced team
- Transparent and smooth progress
- Do it right the first time
- Less duplicated work, re-work and extra work
- Productivity increase
Manage risks and complexity
- Manage risks effectively and in time
- Develop increasing functionality in reduced time
- Handle Functional Safety (ISO 26262) with proven structure
- Integrate Automotive SPICE Plugins (HW SPICE, Mechanical SPICE, Cybersecurity, etc.)
Meet customers' expectation – current and future business
- Avoid penalty (payments and/or negative awareness)
- Win quotations (positive supplier ranking, flexibility)
For your own sake
- Less priority hopping
- Clear responsibilities
- Pride in one's own work
- Less discussions
- No double work
![]()
What is the difference between Automotive SPICE and ISO 26262?
ISO 26262 is a functional safety standard for the development of safety-critical automotive systems. It outlines the processes and conditions for developing safe components in automobiles. Automotive SPICE brings process improvement and process capability determination to the table. Theoretically projects could implement ISO 26262 without Automotive SPICE, but without ASPICE capability level 2 (managed) and CL3 (established) it becomes very difficult to keep the quality high throughout the project life-cycle.
HARA (Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment) is an important part of the ISO 26262 standard. HARA is a systematic and structured process used to identify and evaluate potential hazards and risks associated with the development and use of a safety-critical system. ASIL (Automotive Safety Integrity Level) is a risk classification system ranging from A (lowest risk) to D (highest risk), with each level corresponding to a set of requirements and processes for ensuring the safety of the system.
Safety relevant projects are usually developed with Automotive SPICE. The base practices and generic practices help to build proven processes producing quality output. At the end of the delivery stands the safety case, a document that states the safety risks known in the component. ASPICE forces the development team into a systematic approach to test all requirement with the relevant test methods required in ISO 26262. A good ASPICE rating underlines then the quality of the test reports.
![]()
What is the in ASPICE plug-in concept?
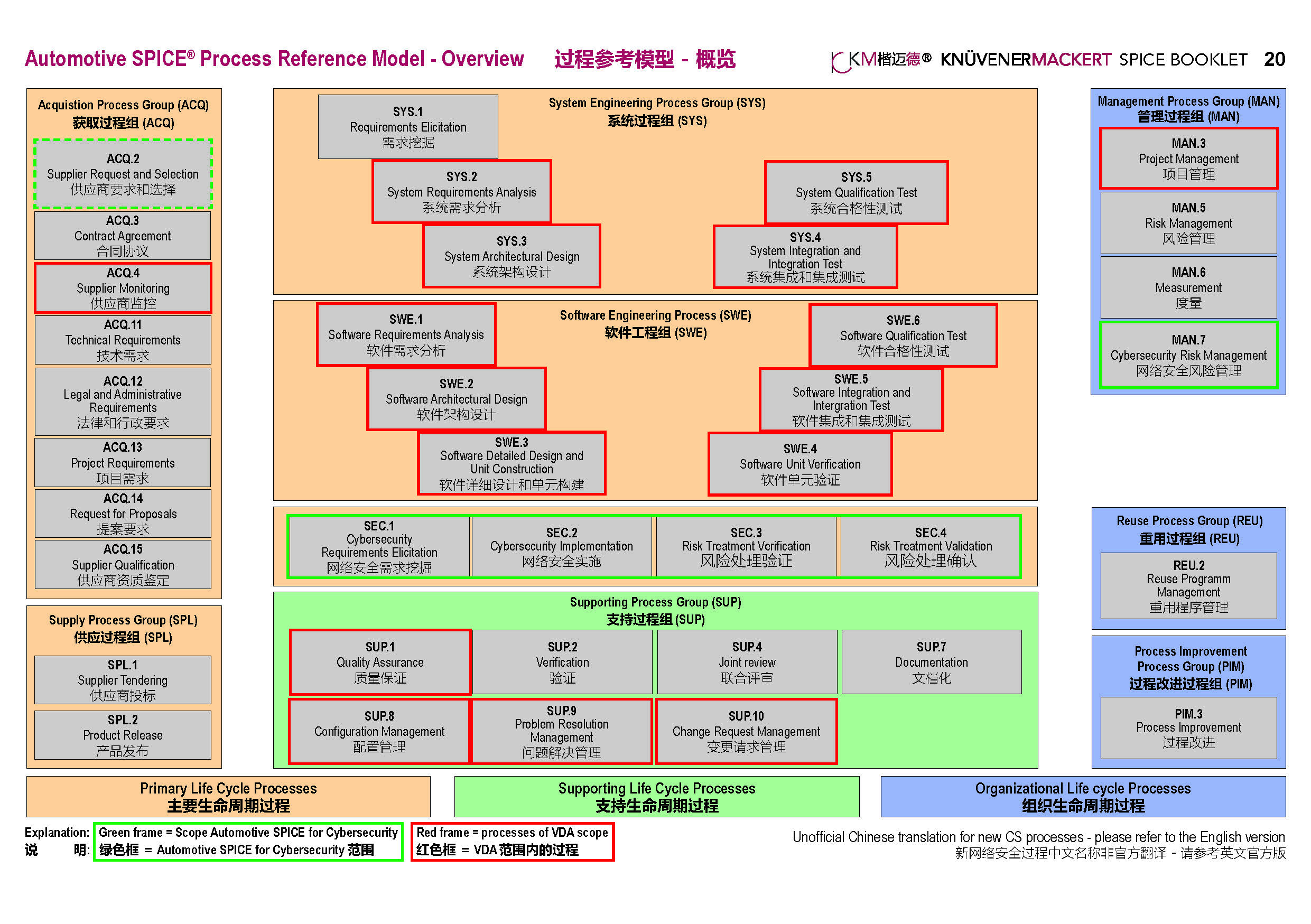
Automotive SPICE is in a sense two-dimensional. The first dimension are the process groups and processes. The VDA scope describe the typical selection of processes. The second dimension are the capability levels. CL1 are process specific base practices. CL2-5 describe generic practices that all processes inherit.
Cybersecurity for Automotive SPICE is one of the plugins. SEC.1-4 MAN.7 and ACQ.2 are additional to the VDA scope.
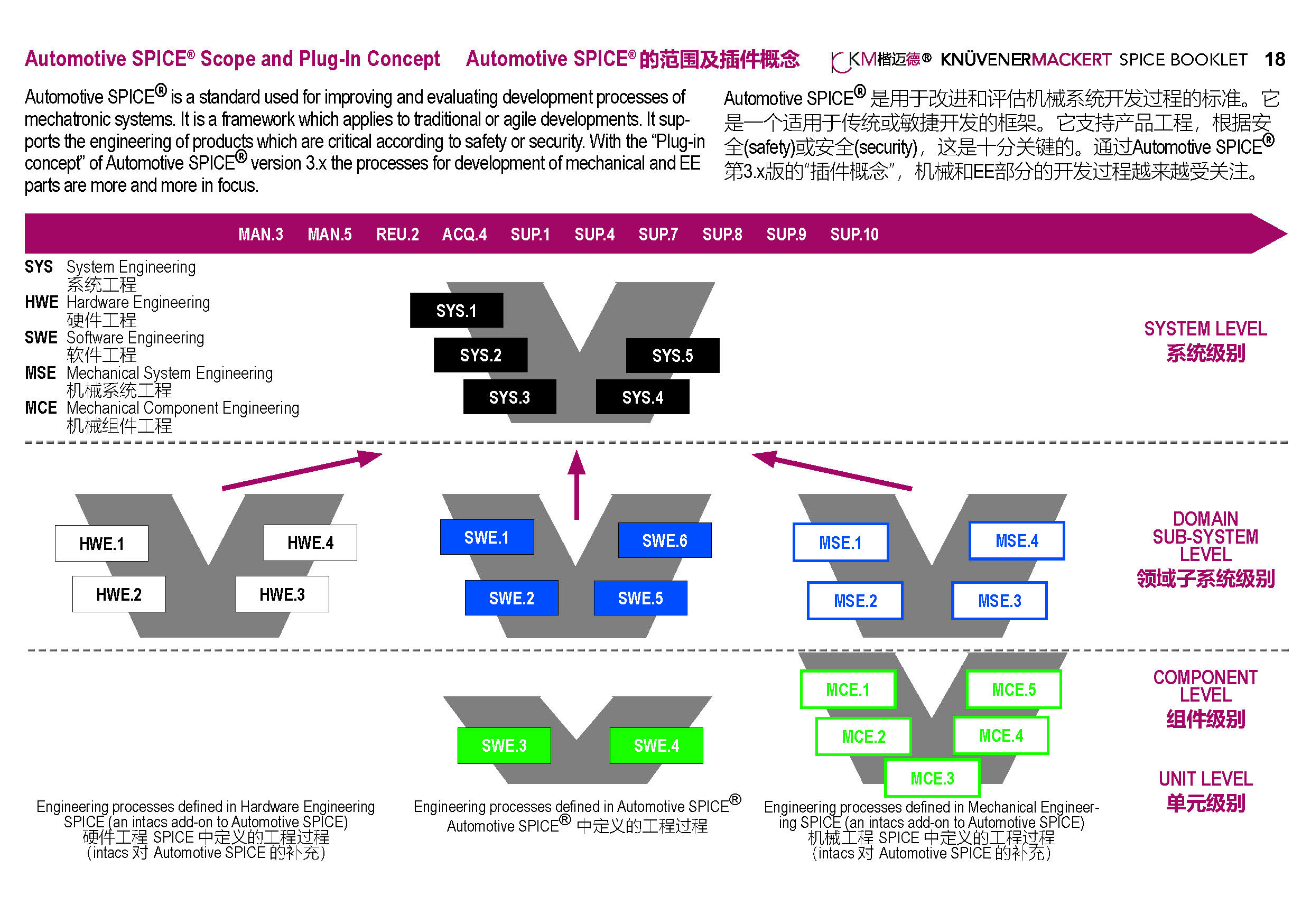
The typical V in the engineering processes can be separated into the system level and the lover domain/component/unit level. Only the system links to stakeholder requirements. It describes the integrated system of often SW, HW and Mechanical components.
Automotive SPICE in the VDA scope only describes the software processes in the domain level. With the plug-ins, hardware and mechanical processes can be rated in ASPICE assessments accordingly.
Automotive SPICE® (System/Software Process Improvement and Capability dEtermination) is an industry standard introduced to help OEMs and their suppliers to manage the complexity in processes based on best practices and lessons learned.
Automotive SPICE is a process assessment model (PAM). ISO 33002 is the norm for assessments. These assessments use a PAM as reference to compare the process activities in a real project of a software based system with the base practices (capability level 1) and the generic practices (CL 2-5). The process ratings with their evidences is then documented in the assessment report signed by the lead assessor.
With growing complexity in car components, most car manufactures and their TIERs require development in line with Automotive SPICE (ASPICE) capability level CL2 or even CL3. Projects have often hundreds of engineers involved. Thousands of requirements need to be analyzed and later qualified in system tests. Processes in line with Automotive SPICE ensure quality output in line with defined milestones.
Automotive SPICE® is a trademark of VDA QMC www.automotivespice.com.
The process assessment model (PAM) of Automotive SPICE defines base practices for capability level CL1 and general practices for higher capability levels. In ASPICE assessments, the rating of these practices is used to determine the capability level of a particular process in the assessment scope.
There are five capability levels: CL1 – Performed. CL2 – Managed. CL3 – Established. CL4 Predictable. CL5 – Innovating.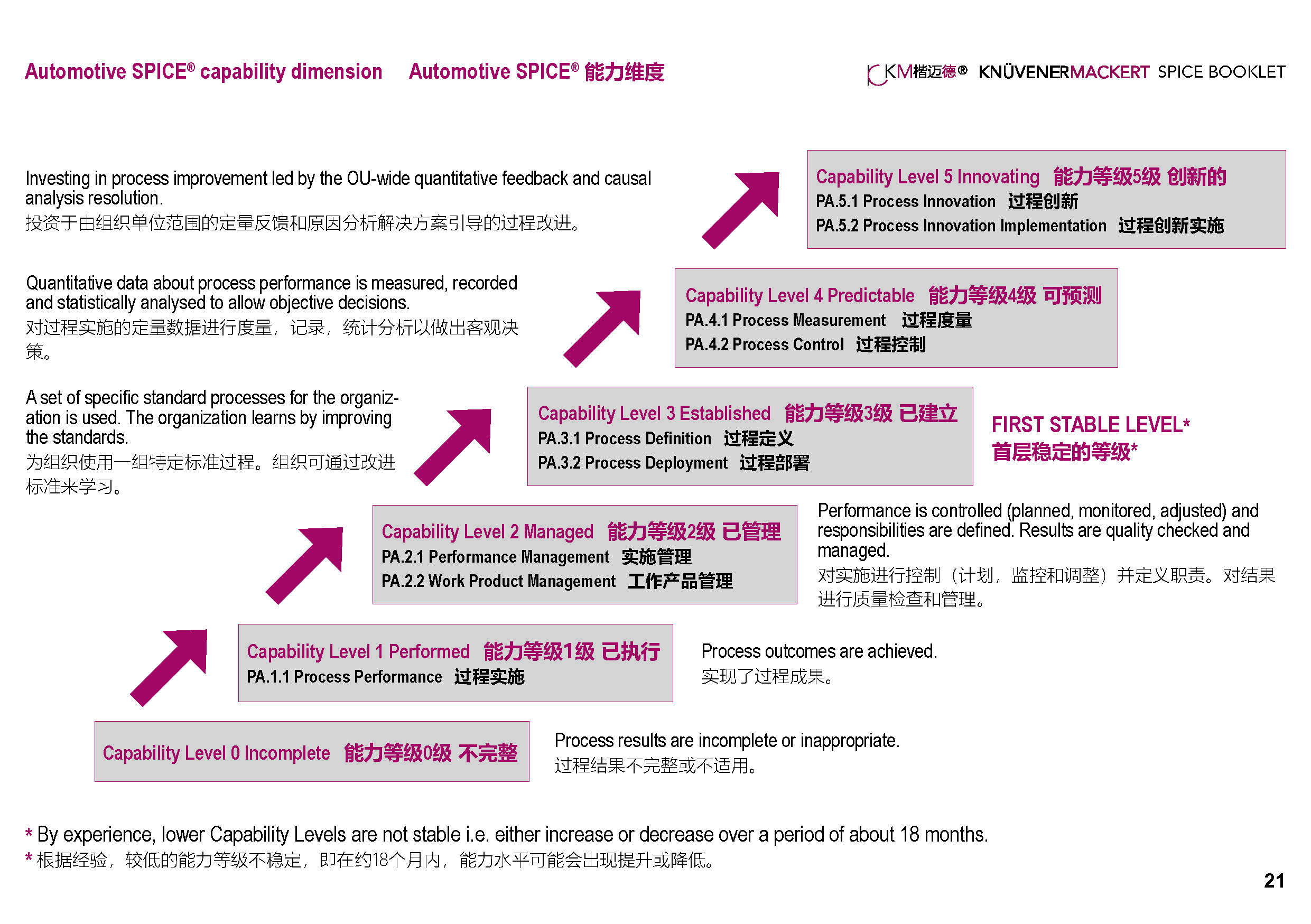
ABC